Fioricet contains a combination of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine Acetaminophen is a pain reliever and fever reducer. Butalbital is in a group of drugs called barbiturates.
It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache. Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant. It relaxes muscle contractions in blood vessels to improve blood flow.
Fioricet is used to treat tension headaches that are caused by muscle contractions.
Fioricet may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.

Fioricet side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to Fioricet: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.

In rare cases, acetaminophen may cause a severe skin reaction that can be fatal. This could occur even if you have taken acetaminophen in the past and had no reaction. Stop taking this medicine and call your doctor right away if you have skin redness or a rash that spreads and causes blistering and peeling. If you have this type of reaction, you should never again take any medicine that contains acetaminophen.
Stop using this medicine and call your doctor at once if you have:
-
- confusion, seizure (convulsions);
- shortness of breath;
- a light-headed feeling, like you might pass out; or
- nausea, upper stomach pain, itching, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Common Fioricet side effects may include:
-
- drowsiness, dizziness;
- feeling anxious or restless;
- drunk feeling; or
- sleep problems (insomnia).
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I take Fioricet?
Take Fioricet exactly as prescribed. Follow all directions on your prescription label. Do not take more of this medication than recommended. An overdose can damage your liver or cause death. Tell your doctor if the medicine seems to stop working as well in relieving your pain.
Butalbital may be habit-forming. Never share Fioricet with another person, especially someone with a history of drug abuse or addiction. Keep the medication in a place where others cannot get to it. Selling or giving away Fioricet is against the law.
Take Fioricet with food or milk if it upsets your stomach.
Store Fioricet at room temperature away from moisture and heat.
Keep track of the amount of medicine used from each new bottle. Butalbital is a drug of abuse and you should be aware if anyone is using your medicine improperly or without a prescription.
What should I avoid while taking Fioricet?
This medication can cause side effects that may impair your thinking or reactions. Be careful if you drive or do anything that requires you to be awake and alert.
Avoid drinking alcohol. It may increase your risk of liver damage while taking acetaminophen.
Ask a doctor or pharmacist before using any other cold, allergy, pain, or sleep medication. Acetaminophen (sometimes abbreviated as APAP) is contained in many combination medicines. Taking certain products together can cause you to get too much acetaminophen which can lead to a fatal overdose. Check the label to see if a medicine contains acetaminophen or APAP.
While you are taking this medication, avoid taking diet pills, caffeine pills, or other stimulants (such as ADHD medications) without your doctor’s advice.
You can not take Prescription for a long time, you need find a way to treat your pain without prescription. Exercising is the best way to relieve your pain. because exercising can enhance your immune system and increase your muscle strength and make your nerve strong.
You can also take some natural nutritions to increase your immune system too. Some anti-aging products can also increase your immune ability. You can try USANA Products ro make you strong. I take USANA Essentials every day and I find my health get better and better.
Patient Reviews on Fioricet for Headache
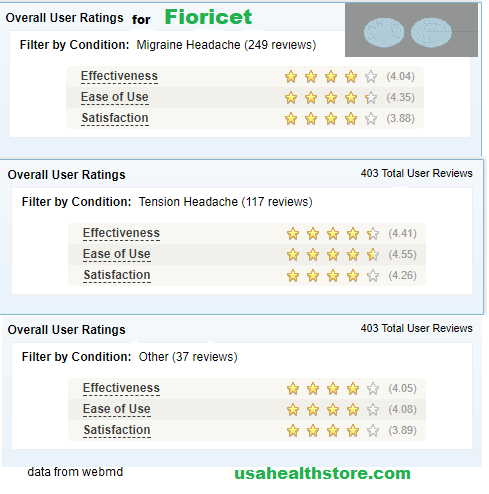
You will find 87% patient rate fioricet is effective for headache relief. But some patients think it is expensive.
One of headache patient reviews fioricet the best medicine for tension headaches bar none. Big pharma has tried to get it banned for years because it is so cheap and effective which is a treat to their vastly over priced, dangerous and ineffective alternatives.
Acetaminophen / butalbital / caffeine Pregnancy Warnings
Use is not recommended unless clearly needed
US FDA pregnancy category: C
Comment: Monitor for barbiturate withdrawal in neonates
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted on this combination product. Epidemiologic data for acetaminophen, including a population based case-control study from the National Birth Defects Prevention Study (n= 11,610) and data from 26,424 live singleton births have shown no increased risk of major birth defects in children with first trimester prenatal exposure. In 2015, the US Food and Drug Administration released results of their evaluation on published research studies looking at mothers who took acetaminophen (either over the counter or as a prescription product) at any time during their pregnancy and the risk of attention deficit hyperactivity (ADHD) in their babies.
They found all studies reviewed had potential limitations in their designs that prevented drawing reliable conclusions. Barbiturates have been reported to readily cross the placental barrier.
A 2-day old infant whose mother had taken a butalbital-containing product during the last two months of pregnancy experienced withdrawal seizures; butalbital was found in the infant’s serum. There are no controlled data in human pregnancy.
US FDA pregnancy category C: Animal reproduction studies have shown an adverse effect on the fetus and there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in humans, but potential benefits may warrant use of the drug in pregnant women despite potential risks.
Acetaminophen / butalbital / caffeine Breastfeeding Warnings
Acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine are excreted into human milk in small concentrations. The significance of the effects on nursing infants has not been reported, but due to the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, other agents may be preferred.
A decision should be made to discontinue breastfeeding or discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Excreted into human milk: Yes (acetaminophen); Yes (barbiturates); Yes (caffeine)
A tablet of Fioricet contains 325 milligrams of acetaminophen, 50 milligrams of butalbital and 40 milligrams of caffeine. Acetaminophen is a pain reliever, butalbital is a barbiturate, and caffeine is a stimulant. The combination of drugs used in Fioricet is also sold under other brand names such as Alagesic, Dolgic, Esgic and Zebutal. All the active ingredients in Fioricet are potentially addictive, especially butalbital.
Physicians usually prescribe Fioricet for headaches caused by muscle contractions. They may also prescribe it for migraine headaches, although the Food and Drug Administration has not indicated it for this purpose. The typical adult dose of Fioricet is one to two tablets every four hours, not to exceed six tablets every 24 hours.
Common Overdose Symptoms
Acetaminophen relieves pain by inhibiting prostaglandin synthetase enzymes, and it has a half-life of no more than three hours. Butalbital depresses the central nervous system and has a half-life of about 35 hours. Caffeine causes the cerebral blood vessels to constrict and has a half-life of about six hours. Mild Fioricet overdose symptoms include the following:
-
-
- Abdominal aches
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Euphoria
- Intestinal problems
- Sedation
- Shortness of breath
- Vomiting
-
Butalbital can also cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome in rare cases, like all barbiturates. This syndrome is a life-threatening skin condition.
Withdrawal from Fioricet
“Withdrawal symptoms of Fioricet occur when you stop taking this drug after becoming dependent upon it.”Withdrawal symptoms of Fioricet occur when you stop taking this drug after becoming dependent upon it. A physician will typically reduce your dosage slowly in order to minimize the withdrawal symptoms, rather than abruptly discontinuing your usage of Fioricet. You may also receive medication to help you taper off Fioricet. Withdrawal symptoms usually begin between 8 and 36 hours after your last dose and may last up to a week or two. Signs of an overdose on Fioricet include the following:
-
-
- Anxiety
- Breathing trouble
- Raised blood pressure
- Elevated body temperature
- Delirium
- Tiredness
- Headaches
- Increased heart rate
- Nausea
- Ringing in the ears
- Shaking
-
Available Treatment Options
In the event of an overdose on Fioricet, call 911 immediately. Emergency treatment is critical to ensure the person remains stable. After the immediate overdose risk is averted, subsequent care is essential to effectively address the drug abuse or addiction issue.
Fioricet rehab treatment normally begins with the detoxification phase. This process reduces the patient’s dosage of Fioricet until they are no longer taking the drug at all. The detoxification phase of the treatment eliminates the patient’s physical dependence on Fioricet. The remainder of a treatment program for Fioricet addiction deals primarily with the psychological aspect of the addiction.


