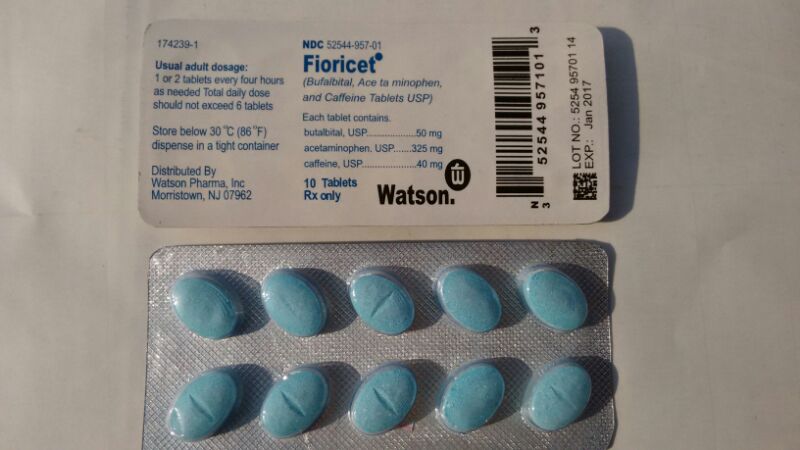
Signs And Symptoms of Fioricet Overdose
As you know, Fioricet contains a combination of acetaminophen, butalbital, and caffeine Acetaminophen is a pain reliever and fever reducer. Butalbital is in a group of drugs called barbiturates. It relaxes muscle contractions involved in a tension headache. Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant. It relaxes muscle contractions in blood vessels to improve blood flow.
Toxicity from barbiturate poisoning includes drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; and hypovolemic shock. Toxicity from codeine poisoning includes the opioid triad of: pinpoint pupils, depression of respiration, and loss of consciousness. Convulsions may occur.
In acetaminophen overdosage: dose dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect.
Renal tubular necrosis, hypoglycemic coma, and coagulation defects may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxicoverdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours postingestion.
Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium, tachycardia, and extra systoles.
Treatment
A single or multiple drug overdose with Fioricet with Codeine is a potentially lethal polydrug overdose, and consultation with a regional poison control center is recommended. Immediate treatment includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, vasopressors, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated.
Assisted or controlled ventilation should also be considered. For respiratory depression due to over dosage or unusual sensitivity to codeine, parenteral naloxone is a specific and effective antagonist.
Gastric decontamination with activated charcoal should be administered just prior to N-acetylcysteine (NAC) to decrease systemic absorption if acetaminophen ingestion is known or suspected to have occurred within a few hours of presentation.
Serum acetaminophen levels should be obtained immediately if the patient presents 4 hours or more after ingestion to assess potential risk of hepatotoxicity; acetaminophen levels drawn less than 4 hours post-ingestion may be misleading.
To obtain the best possible outcome, NAC should be administered as soon as possible where impending or evolving liver injury is suspected.
Intravenous NAC may be administered when circumstances preclude oral administration. Vigorous supportive therapy is required in severe intoxication.
Procedures to limit the continuing absorption of the drug must be readily performed since the hepatic injury is dose dependent and occurs early in the course of intoxication.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. An overdose of Fioricet can be fatal.
The first signs of an acetaminophen overdose include loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, sweating, and confusion or weakness. Later symptoms may include pain in your upper stomach, dark urine, and yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes.
Overdose symptoms may also include insomnia, restlessness, tremor, diarrhea, increased shallow breathing, uneven heartbeats, seizure (convulsions), or fainting.
Acetaminophen Overdose Treatment

What Is Acetaminophen Toxicity?
Acetaminophen (Tylenol®) toxicity is a common cause of acute liver failure in children and adolescents. Acetaminophen, also known as paracetamol and N-acetyl-p-aminophenol (APAP), is primary used for the treatment of pain and/or fever, but is also a component in numerous medications, including Percocet®, Alka-Seltzer® Plus Cold & Sinus, Dayquil®, and Excedrin®. Acetaminophen is an effective pain-relieving and fever-reducing agent when taken in the recommended daily dose.
Acetaminophen toxicity or overdose can occur purposefully (when a person knowingly takes more than the recommended maximum daily dose) or accidentally (when a person is unaware they are taking multiple products containing acetaminophen and exceeds the recommended maximum daily dose).
The maximum recommended acetaminophen dosage is 4 grams/day in an adult and 90 mg/kg/day in children. People with underlying liver disease or those with chronic alcohol consumption are at an increased risk of developing hepatotoxicity (liver damage from chemicals) with use of acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen Toxicity Symptoms
Initial symptoms of acetaminophen toxicity can take up to 12 hours to appear. Symptoms and side effects include:
- Abdominal pain
- Irritability
- Generalized weakness
- Loss of appetite
- Jaundice (yellow appearance of skin and eyes)
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Convulsions
- Coma
Acetaminophen Toxicity Diagnosis
A doctor’s first step in diagnosing acetaminophen toxicity is to get a complete history, including the time the medication was ingested, the amount of medication that was ingested, and what form of the medication was ingested. A diagnosis of acetaminophen toxicity is usually confirmed through diagnostic tests, including an acetaminophen level, electrolytes, kidney function tests, amylase, lipase, liver function tests, complete blood count, and coagulation factors. Imaging studies, such as an ultrasound may be used to assess liver enlargement. A liver biopsy may also be ordered.
Acetaminophen Toxicity Treatment
Timing is a vital factor in the treatment of acetaminophen toxicity, and therefore doctors attempt to begin treatment of acetaminophen overdose within eight hours of ingestion in order to achieve the best possible outcome for the patient. The majority of patients survive acetaminophen toxicity with supportive care such as intravenous fluids and anti-nausea medication, activated charcoal, if used within one hour after ingestion, and antidotal therapy, including N-acetylcysteine (Acetadote®, Mucomyst®).
For patients who fail the above therapies and develop liver failure, liver transplantation may be the only treatment option. Doctors will determine if transplantation is necessary if the above tests are significantly abnormal and the patient has developed hepatic encephalopathy, a disorder of the brain caused by a dysfunctional liver.
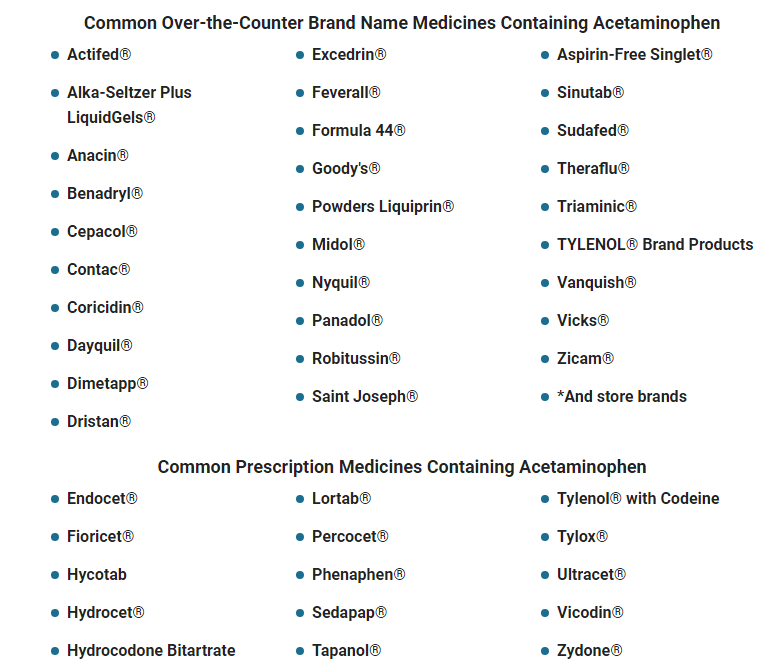
The Medicines that Contain Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is the most common drug ingredient in America. More than 600 medicines contain acetaminophen. These include both prescription medicines and medicines available without a prescription, also called “over-the-counter,” or “OTC” medicines. To prevent acetaminophen overdose, you need to be able to read labels and recognize when their medicines contain acetaminophen. The active ingredients in OTC medicines are clearly listed on the label, and the word “acetaminophen,” is listed on the front of the package or bottle and in the Active Ingredient section of the Drug Facts label. On prescription labels, acetaminophen is sometimes listed as “APAP,” “acetam,” or other shorted versions of the word. To know what is in your medicines, read the list of active ingredients on the label each and every time you take a medicine.
You may be surprised to learn just how many medicines contain this acetaminophen: